Understanding Structural Steel Fabrication
Definition and Importance of Structural Steel Fabrication
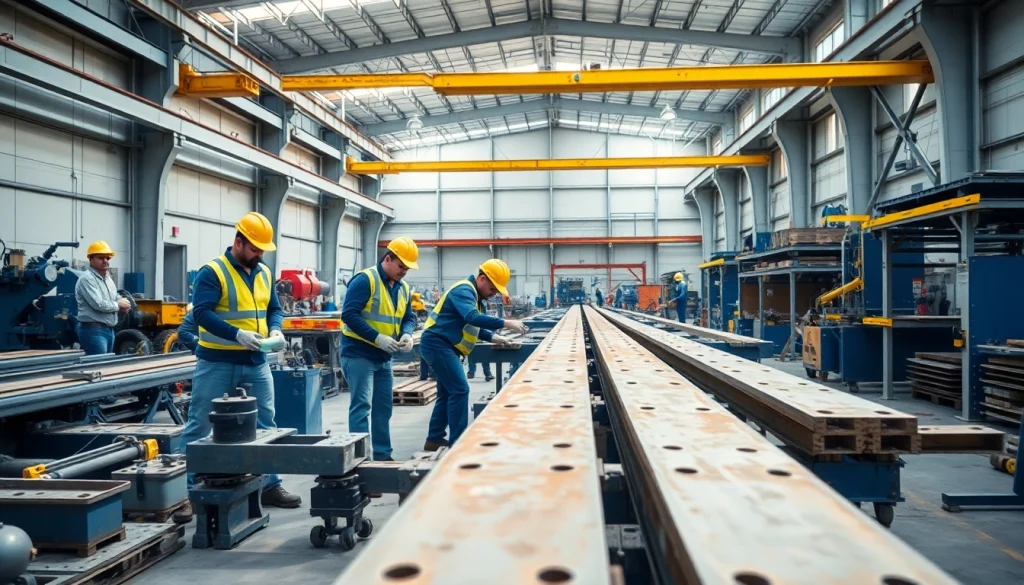
Structural steel fabrication encompasses the processes of cutting, bending, and assembling steel structures to create framework that supports buildings, bridges, and other infrastructures. This process is fundamental in both commercial and industrial construction, ensuring that structures remain durable and structurally sound. Through techniques in structural steel fabrication, builders can customize structures to meet the exact specifications needed for their projects while also adhering to safety regulations and standards.
The importance of structural steel fabrication lies in its ability to provide strength, resilience, and versatility in a wide variety of applications. As buildings grow taller and engineering feats become more ambitious, understanding the nuances of steel fabrication becomes even more crucial. This article delves into various aspects of steel fabrication, its benefits, applications, challenges, and future trends.
Primary Techniques in Structural Steel Fabrication
There are several key techniques involved in the structural steel fabrication process:
- Cutting: This can be performed using various methods such as saw cutting, plasma cutting, and oxy-fuel cutting. Each method has its pros and cons and is chosen based on the specialized needs of the project.
- Bending: Bending is often achieved through press brakes and roll benders. This technique allows steel to be shaped precisely for its intended application, enhancing both aesthetic and structural aspects.
- Welding: A pivotal technique, welding enables the connection of different components together, ensuring structural integrity. Advanced methods, such as MIG and TIG welding, can be employed depending on the required strength and finish.
- Finishing: After the structural components are fabricated, they often undergo surface treatments such as blasting, painting, or galvanizing to enhance durability and corrosion resistance.
Common Materials Used in Structural Steel Fabrication
The primary material in structural steel fabrication is, of course, steel itself, which is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio. However, several types of steel and other materials may be used, including:
- Mild Steel: Typically used for its malleability, mild steel is less expensive than other grades and is suitable for a variety of structural applications.
- High-Strength Steel: This type of steel offers enhanced strength and is commonly used in high-load-bearing structures.
- Stainless Steel: Known for its corrosion resistance, stainless steel is vital for structures exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
- Composite Materials: In some advanced applications, composite materials may be utilized alongside steel to enhance functionality and weight considerations.
Benefits of Structural Steel Fabrication
Cost-Effectiveness of Structural Steel Fabrication
One of the most significant advantages of structural steel fabrication is its cost-effectiveness. Steel has a favorable strength-to-cost ratio, allowing for the construction of structures that are lighter yet equally strong compared to traditional materials such as concrete. Additionally, the speed of fabrication and the ease of assembly translate into reduced labor costs and shorter construction timelines. These factors combined can significantly lower the overall project budget without compromising structural integrity.
Environmental Advantages of Using Steel
Using steel in construction has notable environmental benefits. Steel is one of the most recycled materials globally, and its high recyclability reduces the consumption of raw materials. Additionally, structural steel fabrication processes often lead to less waste, as steel components can be designed and manufactured to exact specifications, minimizing excess. Lastly, steel’s longevity and durability contribute to the sustainability of buildings, as fewer resources are required for repairs or replacements in the long term.
Durability and Longevity of Steel Structures
Structures made from steel benefit from inherent durability and resistance to various environmental factors, including corrosion, fire, and termites. With proper maintenance and protection measures, steel structures can last for decades without significant degradation. This longevity translates to lower lifecycle costs and fewer disruptions for maintenance, making structural steel a prudent choice for investors and developers alike.
Applications of Structural Steel Fabrication
Commercial Buildings and Infrastructure
In commercial buildings, structural steel fabrication plays a pivotal role in creating high-rise offices, warehouses, and retail spaces. Its strength allows for large spans and open floor plans, essential for modern architecture. Additionally, steel fabrication is fundamental in constructing critical infrastructure such as bridges, highways, and airports, where safety and reliability are paramount.
Industrial Applications of Structural Steel Fabrication
Structural steel fabrication is heavily utilized in industrial facilities, including factories, power plants, and processing plants. Here, steel structures support heavy machinery and equipment, necessitating robust designs capable of withstanding dynamic loads. Customized fabrication allows for optimal integration of operational processes and ease of maintenance within complex industrial environments.
Residential Projects Utilizing Steel
In recent years, the use of structural steel in residential projects has increased significantly. Modern home designs often incorporate open spaces and large windows, achievable through steel frameworks. Steel not only provides structural support but also enhances aesthetic appeal with its sleek lines and contemporary finishes. Moreover, its durability, reduced maintenance requirements, and fire resistance make it particularly appealing to homeowners.
Challenges in Structural Steel Fabrication
Addressing Safety Concerns in Fabrication
Safety is paramount in the steel fabrication industry, with risks associated with heavy machinery, working at heights, and exposure to hazardous materials. To address these concerns, stringent safety protocols must be established, including regular training for workers, proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and adherence to industry regulations. Companies must foster a safety-first culture to minimize workplace incidents.
Managing Costs and Time Efficiency
While the cost-effectiveness of structural steel fabrication is a benefit, managing costs and time is a challenge. Delays in material delivery or unforeseen fabrication issues can extend deadlines and inflate budgets. Effective project management strategies, such as lean construction methodologies, can help streamline processes, reduce waste, and enhance overall efficiency throughout the fabrication and construction phases.
Quality Control Measures in Fabrication
Quality control is essential in ensuring that fabricated steel meets design specifications and safety standards. Implementing rigorous inspection processes during the fabrication stages can prevent defects and rework. Techniques such as non-destructive testing (NDT) can help assess the integrity of welds and materials, providing assurance that the structural components will perform reliably in their applications.
Future of Structural Steel Fabrication
Innovations in Fabrication Technology
The future of structural steel fabrication is poised for significant advancements, driven by technological innovations. Automation in fabrication processes through robotics and state-of-the-art machinery enhances precision while reducing human error. Additionally, the integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM) enables detailed planning and visualization, streamlining coordination among various stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle.
Sustainable Practices in the Steel Industry
Sustainability is becoming a prominent focus in the structural steel industry. As demand for environmentally friendly practices increases, innovations in steel production and fabrication are emerging. Techniques that reduce emissions, optimize energy consumption, and promote recycling are being prioritized. Moreover, the adoption of life cycle assessment (LCA) methods helps evaluate and minimize the ecological impact of steel throughout its lifecycle.
Trends Shaping Structural Steel Fabrication
Several trends are shaping the landscape of structural steel fabrication, including the increasing demand for modular construction techniques. These prefabricated elements allow for rapid assembly on-site, significantly reducing construction times. Additionally, the rise of smart building technologies integrates sensors and IoT connectivity into steel frameworks, allowing for real-time monitoring and improved building performance post-construction.
FAQs about Structural Steel Fabrication
1. What is structural steel fabrication?
Structural steel fabrication involves the process of cutting, bending, and assembling steel to create framework for buildings and infrastructure, ensuring durability and safety.
2. What are the benefits of using structural steel?
Benefits include cost-effectiveness, durability, environmental advantages, and versatility across various applications, making it suitable for diverse projects.
3. What are common methods of steel fabrication?
Common methods include cutting, bending, welding, and finishing, allowing for precise and custom solutions tailored to project requirements.
4. How does structural steel compare to other materials?
Structural steel offers superior strength-to-weight ratio, longevity, and cost-effectiveness compared to materials like wood or concrete, especially for large constructions.
5. What safety measures should be followed in steel fabrication?
Safety measures include using personal protective equipment (PPE), conducting regular safety training, and following industry regulations to minimize workplace risks.