Understanding Structural Steel Fabrication
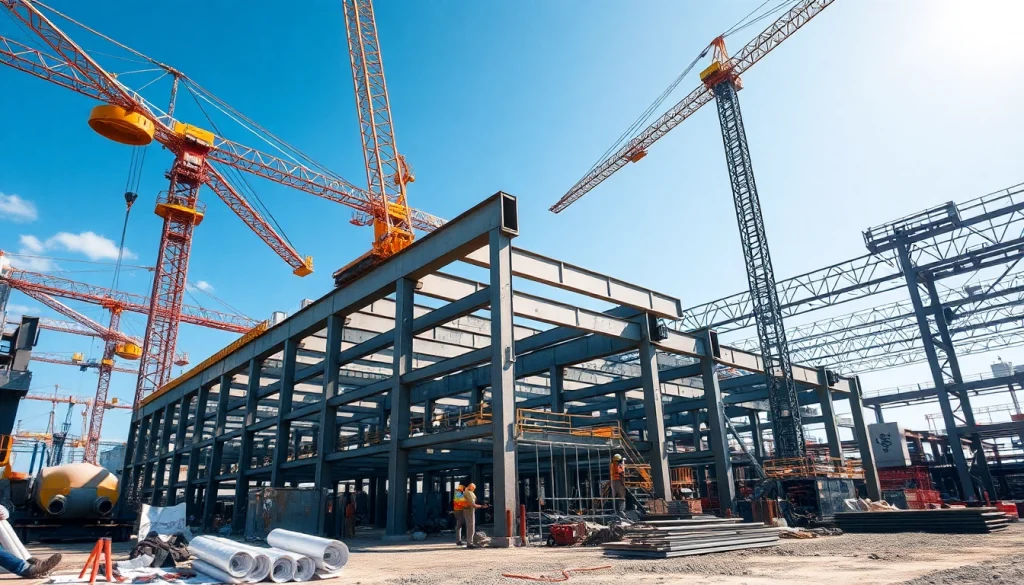
Structural steel fabrication is a critical aspect of modern construction, providing the framework for buildings, bridges, and a variety of structures. This intricate process involves the transformation of raw steel into components that meet precise specifications for strength, durability, and connection. The significance of structural steel fabrication cannot be overstated, as it plays a vital role in ensuring the safety and longevity of constructions we rely upon daily. In this article, we will delve deep into the world of structural steel fabrication, exploring its processes, materials, techniques, best practices, and metrics for success. For an in-depth understanding of structural steel fabrication, read on.
What is Structural Steel Fabrication?
At its core, structural steel fabrication is the process of creating steel structures by cutting, shaping, and assembling steel components. This often starts with raw steel, which is processed according to architectural and engineering drawings to create elements like beams, columns, and trusses. These fabricated components are then delivered to the construction site and assembled to form the overall structure.
The fabrication process is not merely about shaping steel; it involves precise engineering and adherence to strict regulations to ensure safety and stability. Fabricators employ various techniques and tools, resulting in components that can handle loads, withstand environmental stresses, and last for decades. Notably, structural steel is favored for its high strength-to-weight ratio, allowing architects to design taller and more complex structures.
Key Components of the Fabrication Process
The fabrication process can be broken down into several key stages:
- Design and Planning: Engaging with architects and engineers to discuss drafts and specific requirements.
- Material Selection: Choosing the right type of steel and other materials based on desired specifications and project needs.
- Cutting and Shaping: Utilizing saws, lasers, or plasma cutters to create precise shapes from raw steel.
- Welding and Assembly: Joining components using welding methods, bolts, or other techniques to create completed sections.
- Quality Control: Inspecting finished products to ensure they meet ASTM standards and other regulatory guidelines.
- Delivery and Installation: Transporting fabricated elements to the construction site for final assembly.
Importance of Quality Control in Fabrication
Quality control is paramount in structural steel fabrication. Each component must meet specific standards to ensure safety and reliability. Effective quality control processes include:
- Inspection Techniques: Regularly checking dimensions and tolerances using advanced measurement tools such as laser scanners.
- Material Testing: Conducting tests to ensure that the properties of steel (like yield strength and ductility) meet required standards.
- Documentation and Compliance: Keeping detailed records of materials, processes, and inspections to ensure compliance with industry standards.
By implementing stringent quality control measures, fabricators can minimize recall rates and ensure structural integrity, thereby reducing the potential for costly and dangerous failures in the field.
Materials Used in Structural Steel Fabrication
The choice of materials in structural steel fabrication significantly influences the quality and durability of the final product. Understanding the types of steel and their properties is essential for successful projects.
Types of Steel and Their Properties
Various types of steel are utilized in fabrication, each offering unique properties suitable for different applications:
- Mild Steel: Known for its malleability, mild steel is easy to weld and is commonly used in construction.
- High-Strength Low-Alloy Steel (HSLA): This steel is stronger and lighter than mild steel, making it ideal for structures requiring a high strength-to-weight ratio.
- Stainless Steel: With excellent resistance to corrosion and staining, stainless steel is often used in environments where aesthetics and durability matter.
- Tool Steel: Recognized for its hardness and resistance to abrasion, tool steel is employed for creating cutting tools and dies.
- Weathering Steel: This steel has a unique ability to develop a protective layer of corrosion, making it perfect for exposed structures.
Choosing the Right Materials for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate materials for construction is a multifaceted decision that depends on several factors:
- Load Requirements: Understanding the loads a structure must support is critical in choosing the right steel type.
- Environmental Conditions: Factors such as weather, humidity, and exposure to specific elements can influence material selection.
- Aesthetics: The visual characteristics of the materials can impact design decisions, particularly for projects in urban settings.
- Cost Considerations: Balancing budget constraints with the necessity for high-quality materials is always a challenge in fabrication.
Ultimately, a careful assessment of these factors will ensure that the chosen materials can withstand the environment and stresses imposed upon the structure.
Environmental Considerations in Material Selection
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important aspect of construction, environmental considerations have gained prominence in material selection:
- Recyclability: Steel is one of the most recycled materials in the world, making it a sustainable choice for environmental awareness.
- Energy Consumption: Evaluating the lifecycle energy use of materials can help in selecting options that contribute to reducing carbon footprints.
- Eco-Friendly Coatings: The application of non-toxic coatings for corrosion resistance can also impact the sustainability of projects.
Incorporating eco-friendly choices not only aligns projects with environmental standards but can also enhance public perception and compliance with regulations.
Techniques and Methods in Structural Steel Fabrication
The success of structural steel fabrication hinges on the techniques and methods employed during the process. Understanding the pros and cons of these methods is essential for optimizing quality.
Welding vs. Bolt Connections: Pros and Cons
Joining methods in structural steel fabrication typically involve welding or bolts, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages:
- Welding:
- Pros: Offers seamless connections, resulting in a stronger and more aesthetic finish suitable for critical load-bearing elements.
- Cons: Requires skilled labor and proper conditions, as welding can introduce weaknesses through heat distortion.
- Bolted Connections:
- Pros: Easier to assemble and disassemble, making modifications simpler. Generally, requires less skill than welding.
- Cons: May compromise overall structural integrity if not designed properly, particularly in high-load situations.
Making the choice between these methods should be based on project specifications, budget, and environmental factors.
Cutting and Shaping Techniques
The cutting and shaping of steel are essential aspects of the fabrication process. Various methods are employed based on precision needs and available equipment:
- Plasma Cutting: Uses ionized gas to cut steel efficiently, ideal for intricate shapes and designs.
- Oxy-Fuel Cutting: A traditional cutting method that utilizes a flame to melt through steel but is less efficient than plasma cutting for thick materials.
- Laser Cutting: Highly precise and versatile for complex geometries, but can be cost-prohibitive for large-scale operations.
Considering the project’s demands, selecting the right cutting technique can result in more efficient fabrication and better quality components.
Innovative Technologies in Steel Fabrication
Technology has revolutionized the structural steel fabrication industry. Emerging technologies are driving efficiency and accuracy:
- BIM (Building Information Modeling): This digital representation of physical and functional characteristics helps optimize the design and execution processes.
- Robotics and Automation: Increasingly used for repetitive tasks in fabrication shops, thereby reducing human error and increasing production rates.
- 3D Printing: Emerging as a viable method for creating complex steel components rapidly, with fewer waste materials.
Investing in innovative technologies not only increases productivity but also lowers costs and improves the overall quality of fabricated components.
Best Practices for Effective Structural Steel Fabrication
Implementing best practices ensures that structural steel fabrication projects are completed efficiently and safely. The following principles guide successful fabrication efforts:
Planning and Design Principles
Effective planning and design are cornerstone elements of successful steel fabrication:
- Collaboration: Engage architects, engineers, and fabricators early in the design process to build a mutually beneficial understanding of project goals.
- Modular Design: Consider designing components in modules to simplify assembly and enhance quality checks before reaching the job site.
- Detailed Documentation: Ensure that complete and precise documentation is available for each project phase to avoid misunderstandings and errors.
Managing Project Timelines and Resources
Timely delivery and effective resource management are vital in construction. Key strategies include:
- Establishing Milestones: Set clear milestones throughout the fabrication process which helps in evaluating performance along with tracking progress.
- Resource Allocation: Manage stock levels and labor efficiently to prevent bottlenecks, ensuring that materials are available when needed.
- Agility: Build flexibility into project plans to adapt rapidly to changes, whether in design requirements or external factors.
Safety Standards and Regulations
Ensuring safety in the fabrication process is non-negotiable. Compliance with regulations is essential to protect workers and maintain operational integrity. Key aspects include:
- OSHA Standards: Adhering to Occupational Safety and Health Administration guidelines to ensure a compliant and secure workplace.
- Regular Training: Conducting safety training sessions for staff to ensure they understand safety practices and emergency protocols.
- Risk Assessments: Regular assessments of job sites and processes to identify potential hazards and implement practical solutions.
Fostering a culture of safety not only protects employees but also enhances productivity by reducing incidents that can cause downtime.
Measuring Success in Steel Fabrication Projects
Ultimately, measuring the success of structural steel fabrication projects involves evaluating performance metrics and focusing on continuous improvement. Here’s how to gauge success effectively:
Performance Metrics for Fabrication Processes
Establishing quantitative performance metrics provides a clear framework to assess the overall success of projects:
- On-Time Delivery: Measuring adherence to timelines can help ensure that projects remain on schedule and within budget.
- Quality Compliance Rate: The percentage of components passing quality inspections can provide insights into the effectiveness of quality control processes.
- Cost Variance: Comparing projected costs to actual expenditure helps identify areas for potential savings and efficiency improvements.
Case Studies: Successful Fabrication Projects
Evaluating real-life examples of successful steel fabrication projects can yield insights and best practices that one can apply to future endeavors. Typically, case studies encompass challenges faced, the strategies employed, project timelines, and outcomes, providing a wealth of learning opportunities.
Continuous Improvement in Fabrication Techniques
Emphasizing continuous improvement fosters innovation and efficiency in the fabrication process:
- Feedback Loops: Set up mechanisms for gathering and analyzing feedback from projects to inform better practices going forward.
- Benchmarking: Compare processes and results against industry standards to target areas needing enhancement.
- Investing in Training: Keep employees updated on the latest techniques and technologies to enhance their skills and efficiency.
By committing to ongoing learning and innovation, companies can stay competitive in the evolving industry landscape.